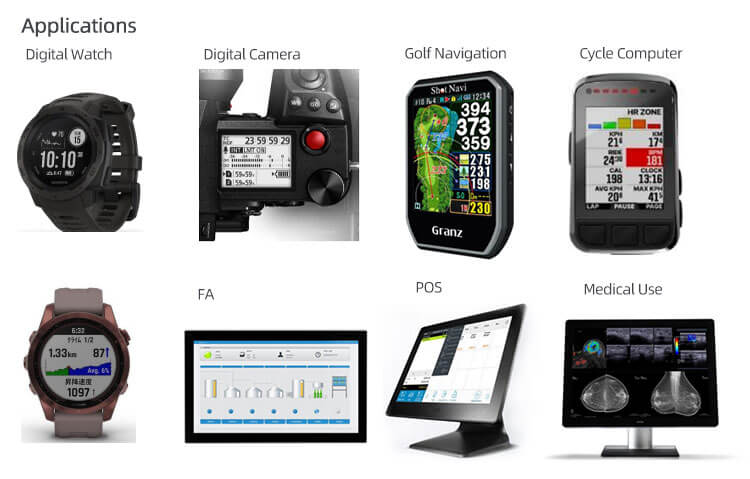
Writer: adminRelease Time: 2024-11-20 08:20Browse: 1065
LCD display technology, the full name of which is Liquid Crystal Display, is a technology that uses the optical properties of liquid crystal materials to change the transmittance of light by controlling the electric field to achieve image display. The following is a detailed explanation of the working principle of LCD display technology:
The LCD display is mainly composed of polarizers, liquid crystal layers, electrodes and backlight modules. The liquid crystal layer is located between two parallel glass substrates, on which there are many vertical and horizontal fine wires, which are used to control the arrangement direction of liquid crystal molecules by whether they are powered on or not.
The arrangement of liquid crystal molecules: In the natural state, liquid crystal molecules are long rods with their long axes roughly parallel. When liquid crystal is poured between two planes with fine grooves, the grooves on the two planes are perpendicular to each other (intersecting at 90 degrees), so that the liquid crystal molecules are forced into a 90-degree twisted state between the two planes.
The role of the electric field: When an electric field is applied to the LCD, the arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules will change. Specifically, the liquid crystal molecules will rearrange vertically so that the light can be emitted directly without any twisting. In this way, by controlling whether the electric field is applied or not, the arrangement state of the liquid crystal molecules can be controlled, and then the transmittance of light can be controlled.
Refraction and transmission of light: When light passes through liquid crystal, it will be twisted 90 degrees by the liquid crystal molecules. But after the electric field is applied, the liquid crystal molecules are rearranged so that the light can pass directly without twisting. With components such as backlight and filter, the image can be displayed.
Pixel control: Each LCD pixel is composed of three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue (RGB). By precisely controlling the light intensity of these three sub-pixels, different colors and brightness can be mixed to form a complete picture.
Low power consumption: Since LCD uses liquid crystal molecules as display elements, its power consumption is much lower than that of traditional CRT displays.
Rich colors: By precisely controlling the light intensity of the three RGB sub-pixels, LCD can display rich colors and delicate images.
Fast response speed: With the continuous advancement of technology, the response speed of LCD has been significantly improved, which can meet the needs of various dynamic image displays.
Viewing angle limitation: Although the viewing angle of LCD is constantly improving, there is still a certain viewing angle limitation. To solve this problem, manufacturers have developed a variety of wide-angle technologies, such as TN+FILM, IPS (IN-PLANE -SWITCHING) and MVA (MULTI-DOMAIN VERTICAL alignMENT).
In summary, LCD display technology controls the electric field to change the arrangement of liquid crystal molecules, thereby controlling the transmittance of light to achieve image display. Its working principle is simple and effective, making LCD an important display technology widely used in TVs, computer monitors and mobile devices.