Touchscreen control primarily relies on the collaborative work of hardware components (such as touch sensors and controllers) and software (drivers, operating systems, and applications). Its core principle is to detect touch positions and convert signals into recognizable instructions. The following is a step-by-step explanation of the specific control mechanism: Touch Sensor (Detecting Touch Input) Resistive Touchscreen: Consists of two layers of transparent conductive film (ITO coating). Touching causes a change in current between the two layers, and the voltage change determines the coordinates. Capacitive Touchscreen: Utilizes the principle of human body current sensing. When a finger touches the screen, it changes the electric field distribution on the screen surface. The sensor detects the change in charge to determine the position. Infrared Touchscreen: Forms a grating grid through infrared emitters and receivers. Touching blocks specific infrared rays, thus determining the position. Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Touchscreen: Utilizes ultrasonic waves propagating on the screen surface. Touching absorbs some of the sound waves, and the coordinates are determined […]
2025-11-14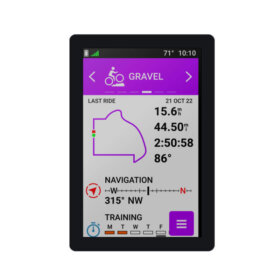
Ultra High Brightness Displays are specialized screens designed to stay clearly visible even in very bright environments, such as under direct sunlight or in outdoor settings. These displays are commonly used in digital signage, outdoor kiosks, transportation hubs, and storefront advertising. Brightness in displays is measured in nits (or cd/m²). A standard indoor monitor has around 250–350 nits Typical smartphones reach 500–1000 nits. Ultra High Brightness Displays often range from 2,000 to over 5,000 nits, and some specialized outdoor units can exceed 10,000 nits. This extremely high luminance allows the screen content to remain vivid, readable, and color-accurate even under direct sunlight. How They Work Ultra high brightness displays achieve their performance through several design elements: Powerful LED Backlighting – High-intensity LED arrays provide the strong light needed for outdoor visibility. Anti-reflective & Anti-glare Coatings – These minimize reflections and improve contrast in bright environments. High-contrast LCD Panels – Enhanced contrast ratios ensure dark areas remain deep black even under bright conditions. Automatic Brightness Control (ABC) – Sensors adjust screen brightness dynamically depending […]
2025-11-07
An HMI display (Human-Machine Interface display) is a specialized screen that allows humans to interact with machines, systems, or processes in an intuitive visual way. It acts as the communication bridge between an operator and the machinery or equipment being controlled. HMI displays are commonly used in industrial automation, manufacturing plants, smart buildings, vehicles, and various embedded systems. Key Functions Visualization of Data: HMI displays present real-time information such as temperatures, pressures, speeds, or production counts in graphical form using charts, meters, and status indicators. This makes it easier for operators to monitor complex processes. Control Interface: Users can send commands through touch, buttons, or rotary knobs to start or stop machines, adjust settings, or change system parameters. Advanced HMI systems support multitouch gestures similar to smartphones. Alerts and Notifications: They display alarms, error messages, or system faults so operators can respond quickly to issues, improving safety and reducing downtime. Data Logging and Analysis: Many HMIs record operation history, trends, and performance data, which can be […]
2025-10-31
Choosing the right Electronic Label Display (ELD) depends on your application, whether for retail shelves, warehouses, smart offices, or industrial tracking. 1. Display Technology E-Ink (e-paper): Low power, high readability, great for static or slow-changing information like prices and inventory. Excellent visibility under bright light. LCD/TFT: Supports color, backlighting, and animations. Good for dynamic or multimedia content, but consumes more power. OLED: High contrast, vivid colors, thin design. Better for premium or design-focused labels, though costlier. 2. Size & Form Factor Small (1–3 inches): Price tags, product info, name badges. Medium (4–7 inches): Shelf labels, meeting room signage. Large (8+ inches): Warehouse displays, logistics tracking, digital signage. 3. Connectivity RF (e.g., 2.4 GHz, proprietary): Low-power, suitable for centralized retail systems. Wi-Fi: High-speed, flexible, but consumes more power. Bluetooth/BLE: Short-range, mobile-friendly, useful for personal/office labeling. NFC: Good for quick updates or interaction with smartphones. 4. Power Source Coin-cell battery: Typical for E-ink labels, lasting months to years. Rechargeable battery/USB-C: Better for frequently updated or multimedia displays. Energy harvesting (solar/light-powered): Sustainable option for retail/warehouse with strong lighting. 5. Durability & […]
2025-09-28
When choosing a Smart Building Digital Display, the process is less about picking a single screen and more about making sure the display system matches your building’s purpose, environment, and technology ecosystem. Here’s a structured guide: Key Factors to Consider 1. Purpose & Application Lobby / Reception → Large, eye-catching LED or video wall for branding, announcements, wayfinding. Conference / Meeting Rooms → Interactive touch displays, wireless presentation support. Hallways / Elevators → Slim, energy-efficient displays for notices and emergency messaging. Smart Control / Command Centers → High-resolution, multi-screen dashboards. 2. Display Technology LED Wall → Best for large indoor/outdoor installations, scalable size. LCD / IPS Panels → Good for smaller indoor signage, high brightness, clear colors. OLED → Sleek, ultra-thin, high contrast (premium lobbies). E-Paper Displays → Low-power option for meeting room booking or door signs. 3. Size & Placement Ensure screen size fits viewing distance and space (too small = unreadable, too big = wasteful). Placement: wall-mounted, free-standing kiosk, ceiling-hung, or embedded in furniture. 4. Brightness & Visibility Indoor: 300–700 nits is enough. […]
2025-09-17
An LCD module (Liquid Crystal Display module) works by controlling the passage of light through liquid crystal material to display images, numbers, or text. Unlike OLED or LED displays, an LCD does not produce its own light—it relies on a backlight. Here’s a breakdown of how it works step by step: 1. Basic Structure of an LCD Module An LCD module is made up of several key layers stacked together: Backlight unit (BLU): Provides uniform white light (often LED-based). Polarizers (front and rear): Control light polarization so liquid crystals can modulate it. Liquid crystal layer: The active medium that changes orientation under an electric field. Glass substrates with transparent electrodes (ITO): Apply voltage to the liquid crystals. Color filters (RGB): Produce full-color images. Driver ICs (integrated circuits): Control each pixel by applying voltage signals. 2. Working Principle The backlight shines light toward the front of the display. Light first passes through the rear polarizer, which only allows light waves of a certain orientation. The liquid crystal layer is sandwiched between two glass substrates […]
2025-09-12
Micro OLED panels are popular today because they hit the sweet spot between size, performance, and efficiency, making them perfect for modern devices like AR/VR headsets, smart glasses, and other compact electronics. Here’s why they’re in demand: Key Reasons for Popularity Ultra-High Resolution in Tiny Size Micro OLEDs can pack millions of pixels into a display smaller than a fingernail. This makes them ideal for near-eye displays (like VR/AR) where pixel density must be extremely high to avoid the “screen-door effect.” Exceptional Image Quality Deep blacks, high contrast, and vivid colors thanks to OLED’s self-emissive nature. Fast response time → smooth motion, crucial for gaming, AR, and VR. Energy Efficiency Consumes less power than LCDs for the same brightness. Extends battery life for portable, always-on wearables. Thin & Lightweight No need for bulky backlights. Enables sleek designs in glasses, headsets, cameras, and medical tools. Expanding Applications Beyond AR/VR: used in medical imaging, military optics, industrial head-mounted displays, and automotive HUDs. Also entering consumer electronics like smart viewfinders and […]
2025-09-04
E-ink (electronic ink) displays come in several types, each optimized for different applications. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of e-ink displays: 1. Monochrome E-Ink (Black & White) Description: The most common and widely used type. Shows text and simple graphics in black and white. Applications: E-readers like Amazon Kindle, basic electronic shelf labels (ESL), industrial devices. Advantages: Low power, high readability in sunlight, cost-effective. Limitations: No color, limited refresh rate. 2. E-Ink Grayscale Description: Similar to monochrome but supports multiple levels of gray (4–16 shades). Applications: E-readers that want to display images with shading, medical/industrial displays. Advantages: Better visual depth than pure black & white. Limitations: Still no full color, slow refresh. 3. Color E-Ink (E Ink Kaleido / Triton / Gallery) E Ink Triton (older tech) First-generation color e-ink, supports thousands of colors. Rarely used now due to lower saturation and contrast. E Ink Kaleido (Kaleido, Kaleido Plus, Kaleido 3) Uses a color filter layer on top of a monochrome e-ink […]
2025-08-29
A sunlight readable display is a type of screen specifically designed to remain clear and visible when used in bright environments or under direct sunlight. Normally, standard displays (like those in laptops or budget devices) look washed out or nearly unreadable outdoors because sunlight overpowers the display’s brightness and causes glare. A sunlight readable display solves this problem with special design features. Key Features of Sunlight Readable Displays: High Brightness (Nits): Standard displays: ~200–300 nits. Sunlight readable: usually 700 nits and above, often reaching 1000–2500 nits or more. High Contrast Ratio: Strong contrast makes text and images sharp, even against strong ambient light. Optical Bonding: Fills the air gap between the LCD panel and protective glass with transparent adhesive to reduce internal reflections and glare. Anti-Reflective / Anti-Glare Coatings: Minimize mirror-like reflections caused by sunlight. Wide Viewing Angles: Ensures visibility even when the screen is not viewed straight on. Durability: Often combined with rugged designs for outdoor, industrial, military, marine, automotive, and kiosk applications. In simple terms: […]
2025-08-22
An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panel is made up of multiple precisely layered structures, each playing a specific role in producing the final image. From top (viewer side) to bottom (backlight side), the main structures are: Outer Protective Layer (Cover Glass or Plastic) Protects the panel from scratches, impact, and environmental damage. Often includes anti-glare, anti-reflective, or anti-fingerprint coatings. Polarizer Film (Front Polarizer) A special optical filter that allows light waves of only one polarization to pass. Essential for controlling light through liquid crystals. Transparent Electrode Layer (ITO Glass) Made of indium tin oxide (ITO) coating on glass. Forms one set of electrodes to apply voltage to the liquid crystal layer. Alignment Layer Microscopic grooves on the electrode surface that align the liquid crystal molecules in a specific direction before voltage is applied. Liquid Crystal Layer The core active layer. Liquid crystals twist or untwist when voltage is applied, controlling light passage. Second Alignment Layer & Electrode (Opposite Side) Works with the top electrodes to […]
2025-08-15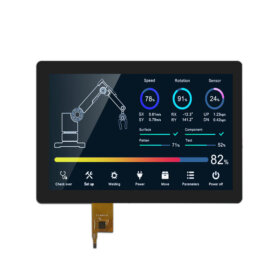
High brightness and high contrast are both important for screen visibility and image quality — but they are very different concepts. High Brightness Definition: Refers to how much light a display emits. Measured in: Nits (cd/m²) Effect: Makes the screen easier to see in bright environments, like sunlight. Helps keep images and text visible when there’s strong ambient light. Good for: Outdoor use (smartphones, kiosks, industrial displays) Fighting screen glare or reflections Too much brightness: Can cause eye strain in low-light conditions. Uses more battery power. High Contrast Definition: Refers to the difference between the darkest black and brightest white on a screen. Measured as: A ratio, e.g., 1000:1, 1000000:1 Effect: Makes details more visible, especially in shadows or dark scenes. Gives depth and realism to images and videos. Good for: Watching movies, reading text, design work Enhancing sharpness and visual clarity Low contrast: Makes images look washed out or dull. Key Differences Table Feature High Brightness High Contrast What it changes Light output of the display Light/dark difference in the image Measured in Nits (cd/m²) Ratio […]
2025-08-08
The three main types of touch screens are: 1. Resistive Touch Screen How It Works: Made of two flexible layers with a gap between. When you press the screen, the layers touch and register a change in resistance at that point. Pros: Works with fingers, gloves, or stylus. Lower cost. Durable against contaminants like dust and water. Cons: Lower light transmission (dimmer display). No multi-touch support. Less sensitive and responsive than capacitive. Common Uses: ATMs, industrial equipment, older GPS devices. 2. Capacitive Touch Screen How It Works: Uses a layer that stores electrical charge. Touching the screen with a conductive object (like a finger) changes the local electrostatic field. Pros: Supports multi-touch. High clarity and responsiveness. Long lifespan with smooth glass surface. Cons: Usually doesn’t work with gloves or non-conductive materials (unless specially designed). More expensive. Common Uses: Smartphones, tablets, interactive kiosks 3. Infrared (IR) Touch Screen How It Works: Uses a grid of infrared light beams across the screen. Touch is detected when the beam […]
2025-08-01
Choosing the right touch sensor for your project depends on several factors related to your application’s needs, environment, user interaction, and technical constraints. 1. Understand Your Application Requirements Type of device: Is it a handheld gadget, industrial machine, kiosk, wearable, or something else? User environment: Will it be used indoors, outdoors, in wet or dirty environments? User interaction: Will users wear gloves? Will they use styluses or fingers? Multi-touch or single touch? 2. Know the Common Touch Sensor Types Resistive Touch: Works by pressure; two conductive layers touch when pressed. Pros: Works with gloves, stylus, cheap, good for harsh environments. Cons: Lower clarity, less durable, no multi-touch. Capacitive Touch (Projected Capacitive, PCAP): Works by sensing electrical properties of the finger or conductive stylus. Pros: Multi-touch, high clarity, durable, responsive. Cons: Usually doesn’t work with gloves unless special gloves or modes are used, more expensive. Infrared (IR) Touch: Uses IR light beams across the screen; touch breaks the beams. Pros: Works with any object, durable. Cons: Can be bulky, […]
2025-07-18
Here's a comprehensive analysis of the waterproof requirements for touchscreens and displays, especially relevant for outdoor, industrial, medical, marine, or rugged applications: The Analysis of Waterproof Requirements for Touch and Displays 1. Importance of Waterproofing Waterproofing is critical for touchscreens and displays used in: Outdoor environments (kiosks, smart parking meters) Industrial applications (factory automation, process control) Medical devices (to allow disinfection and cleaning) Marine and vehicle systems Wearable or handheld devices exposed to moisture, rain, sweat, or cleaning agents Without proper waterproofing, water ingress can lead to: Short circuits Display damage (fogging, corrosion) Touch malfunctions or ghost touches Reduced lifespan and reliability 2. Key Waterproofing Standards and Ratings IP Rating (Ingress Protection) The most common classification system: IP65: Dust-tight, water jets from any direction IP67: Dust-tight, immersion up to 1 meter for 30 minutes IP68: Dust-tight, long-term submersion under pressure IP69K: Protection against high-pressure, high-temperature water jets (ideal for food and pharmaceutical industries) NEMA Ratings (mainly in North America) Similar to IP, but includes corrosion and gasket integrity ratings. 3. […]
2025-07-11
Creating a waterproof touch screen for outdoor and industrial applications requires careful integration of several components and protective design features. 1. Choose the Right Touch Technology Projected Capacitive (PCAP): Best for waterproofing and multi-touch functionality. Works through glass or plastic cover lenses. Resistive Touch: Less ideal outdoors; pressure-based, not suitable for gloved use in rain or when wet. Infrared/Optical Touch: Less reliable in harsh or dirty environments. Recommended: PCAP touch with water rejection algorithms for outdoor/industrial use. 2. Use a Fully Laminated or Optically Bonded Display Optical Bonding fills the air gap between the touch sensor and display with a transparent adhesive: Improves readability in sunlight. Prevents moisture/condensation. Strengthens durability 3. Apply Waterproof Cover Glass or Film Use chemically strengthened glass (e.g., Gorilla Glass) or a tough PMMA layer. Seal the edges with waterproof gaskets or silicone. Thickness: 0.7mm–2mm depending on impact requirements. 4. Ensure IP-Rated Enclosure Design Target IP65, IP67, or IP68 rating depending on exposure: IP65: Protected against low-pressure water jets. IP67: Withstands immersion up to 1m […]
2025-07-04