Writer: adminRelease Time: 2025-05-30 08:37Browse: 614
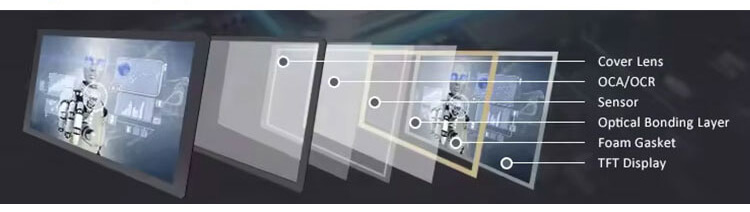
Optical bonding plays a critical role in supporting adhesion, especially in very narrow gaps, such as those found in modern electronic displays. Here's how it works and why it's effective:
Optical bonding is the process of applying a transparent adhesive—typically a liquid optically clear adhesive (LOCA) or optically clear resin (OCR)—between layers in a display stack, such as:
Touch screen and LCD
Cover glass and displays
Display panels and sensor layers
This eliminates the air gap and creates a single, unified optical interface.
In narrow gaps (often less than 1 mm), liquid adhesives can flow naturally due to capillary action, allowing even distribution without trapping air bubbles.
Liquid optical adhesives conform to micro-scale surface irregularities, enhancing contact area and improving adhesive strength even in very thin layers.
Once cured (via UV, heat, or moisture), the adhesive forms a solid bond that maintains adhesion across the entire interface, despite the narrow spacing.
The bonded layer can absorb mechanical stresses caused by drops, temperature fluctuations, or bending—critical in tight assemblies with little mechanical tolerance.
Improved durability – prevents delamination
Better optical clarity – no internal reflections from air gaps
Environmental sealing – keeps out dust, moisture, and particulates
Structural support – reinforces the overall assembly